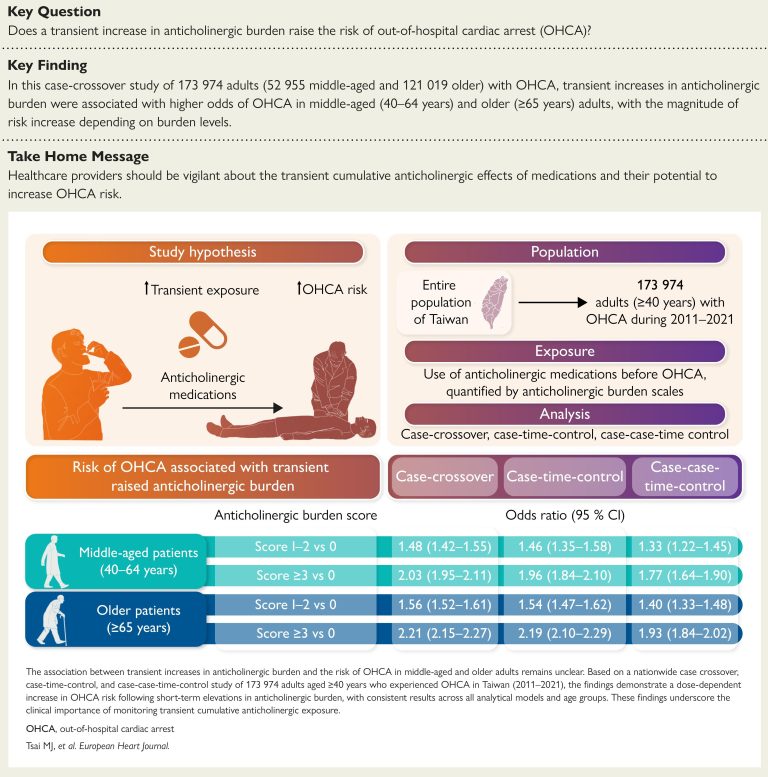
Transient anticholinergic burden and out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
This study examined whether transient increases in anticholinergic burden are associated with a higher risk of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA).
Using a case-crossover design including 173,974 OHCA patients, the results showed that transient increases in anticholinergic burden were associated with higher odds of OHCA among middle-aged and older adults. These findings highlight the importance for healthcare providers to remain vigilant regarding the cumulative, transient anticholinergic effects of medications and their potential role in increasing OHCA risk.